Scientific highlights 2019
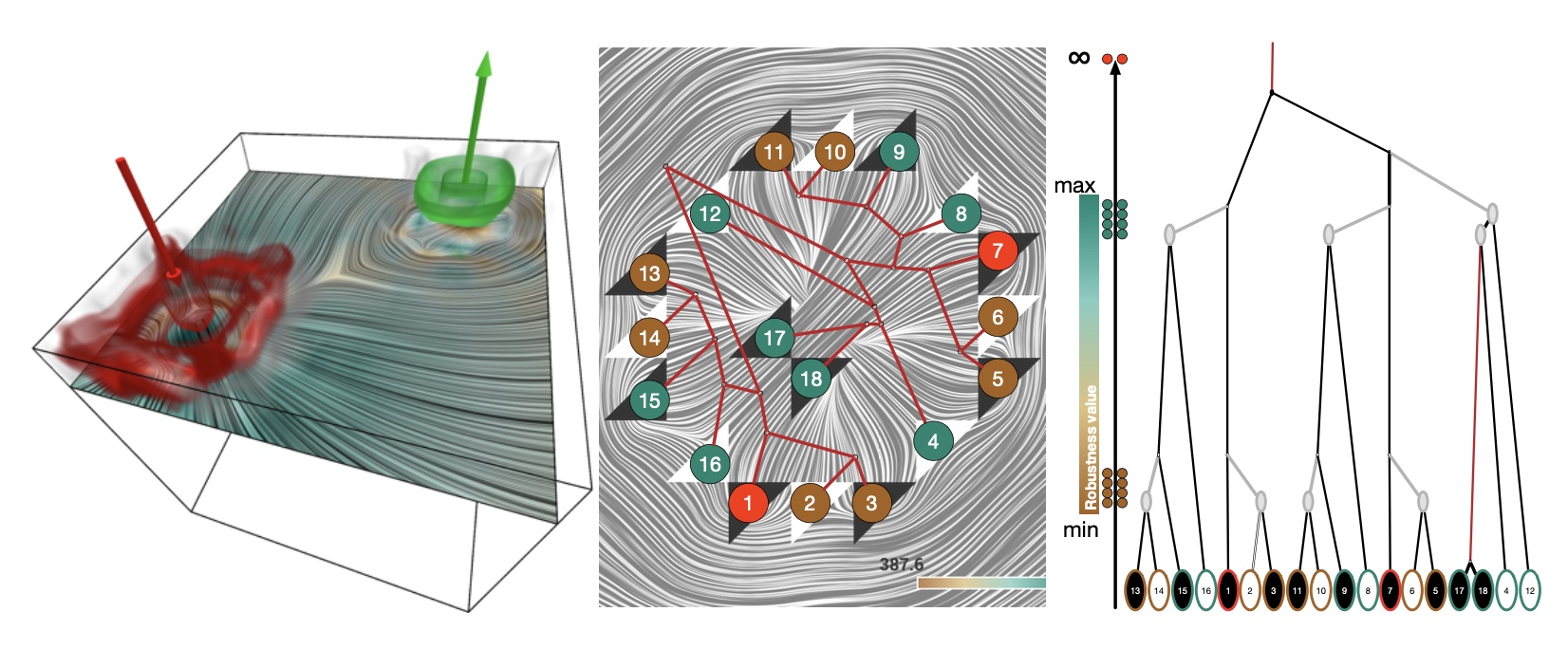
Robust Extraction and Simplification of 2D Tensor Field Topology
Research focus area – Topological methods for dynamical data
Application – Materials for the future
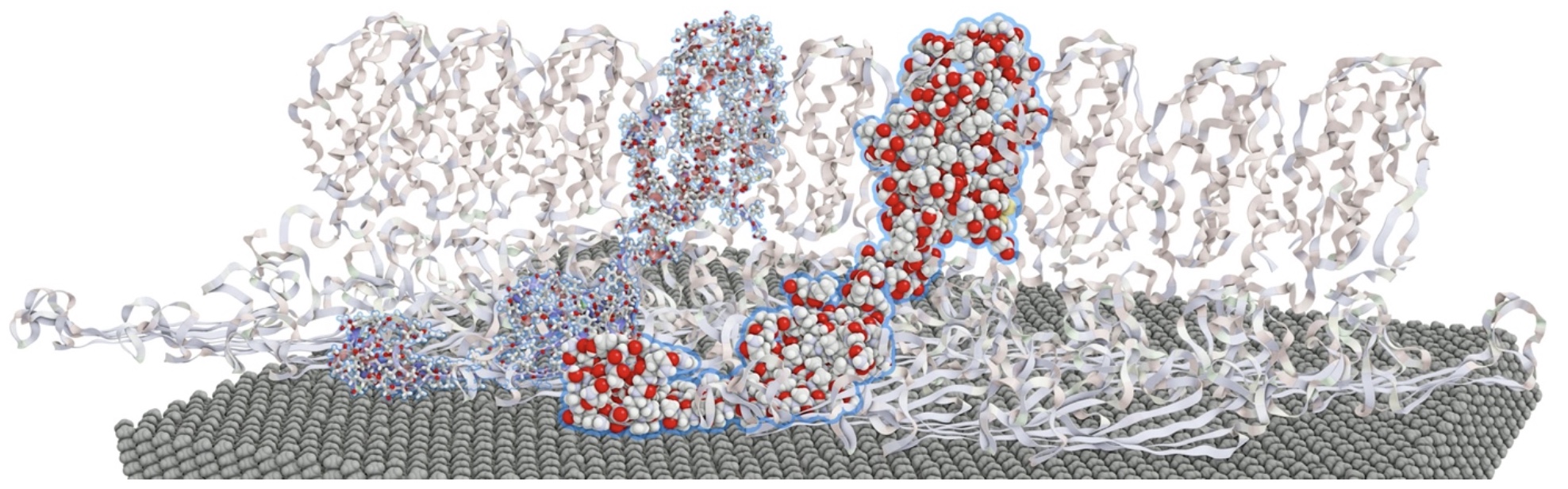
Selection Concepts for Complex Molecular Structures
Research focus area – Multi-scale visualization
Application – Molecular dynamics simulations for conformation analysis
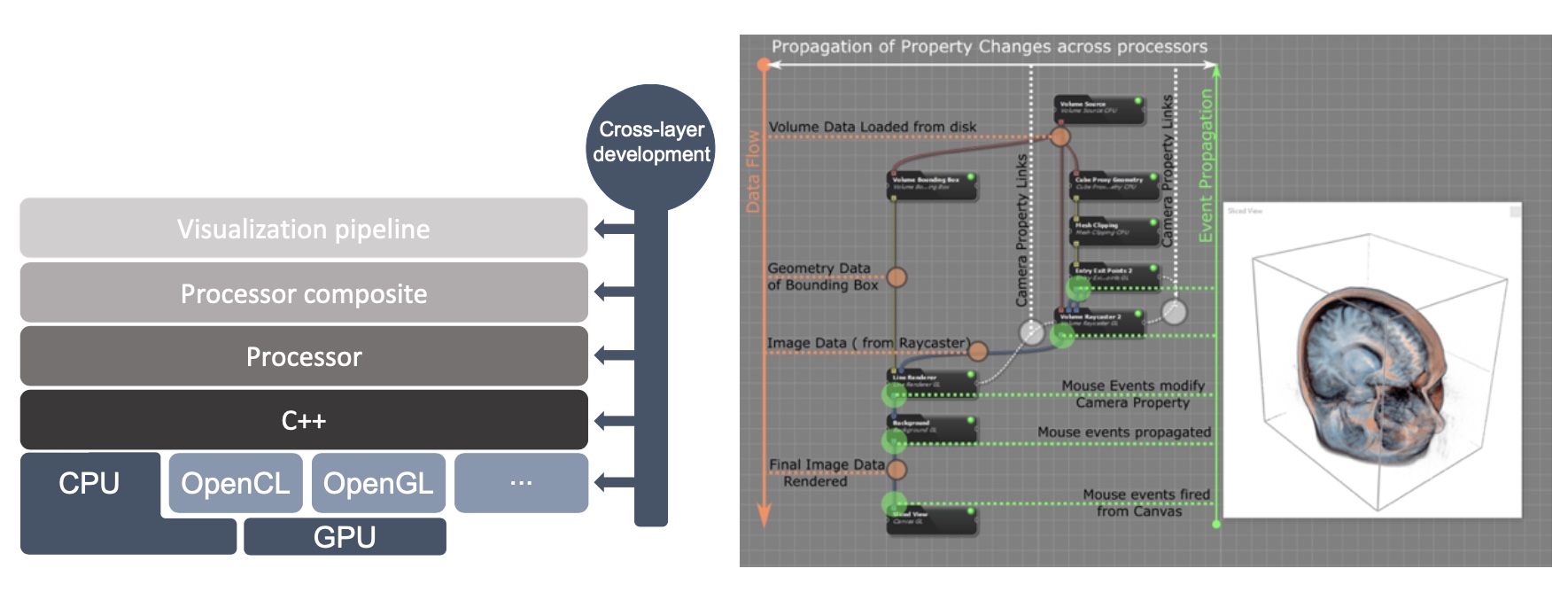
Inviwo – An open-source Visualization System with Usage Abstraction Levels
Inviwo is a software framework for rapid prototyping visualizations. It builds the basis for the development of novel visualization research and teaching
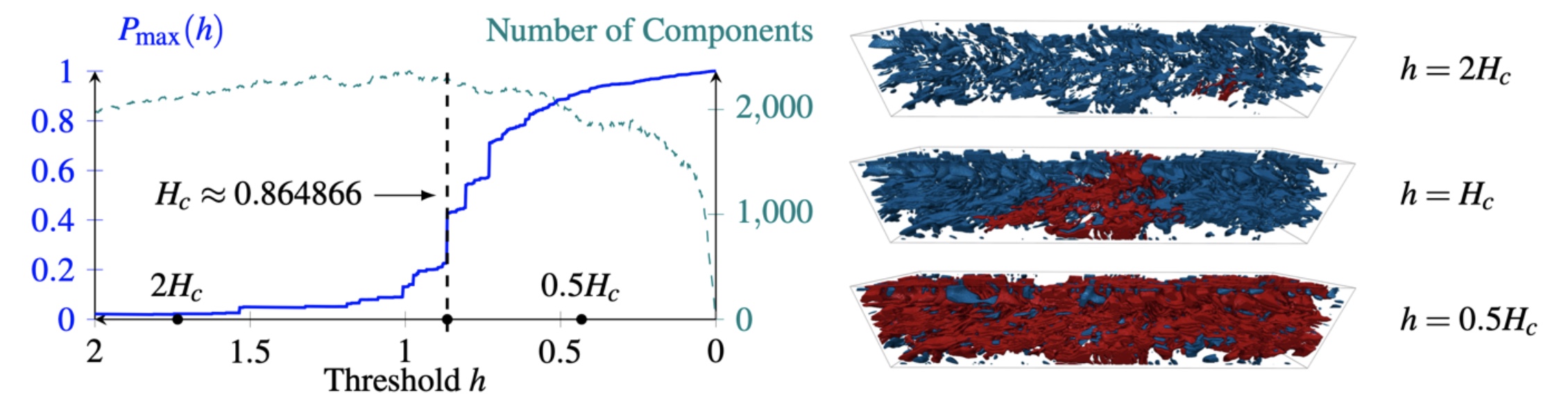
Distributed Percolation Analysis for Turbulent Flows
Turbulent flow analysis plays a crucial role in many domains e.g. design of fuel-efficient cars and is an active research area primarily addressed through direct numerical simulations (DNS) of the Navier-Stokes equations.
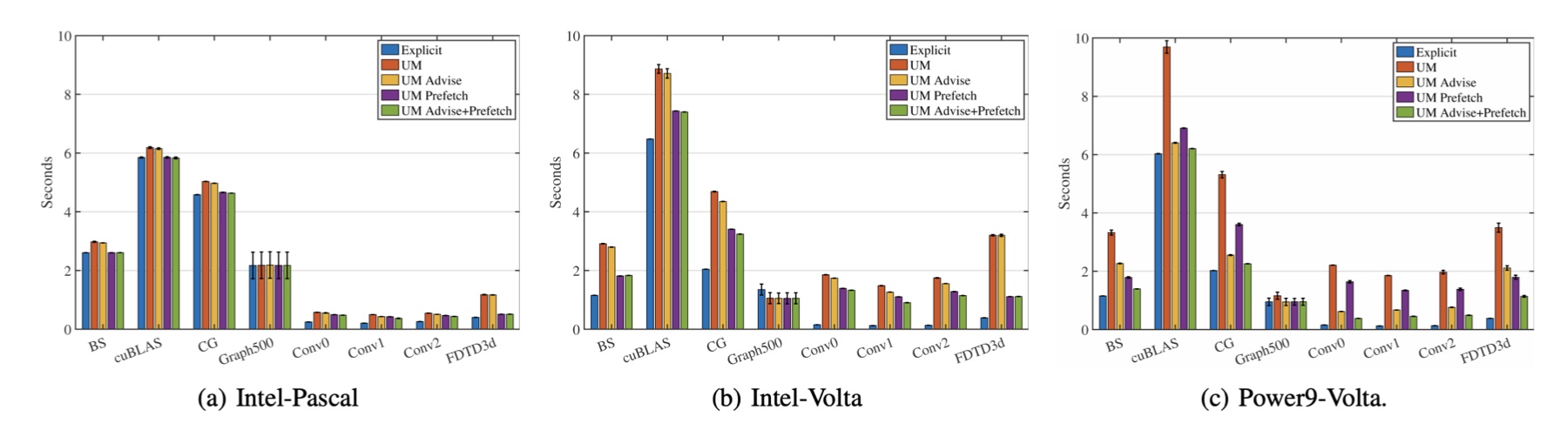
Assessing the Performance Improvements of new Features in CUDA Unified Memory
Recently, leadership supercomputers are becoming increasingly heterogeneous. For instance, the two fastest supercomputers in the world, Summit and Sierra, are both equipped with Nvidia V100 GPUs for accelerating workloads.
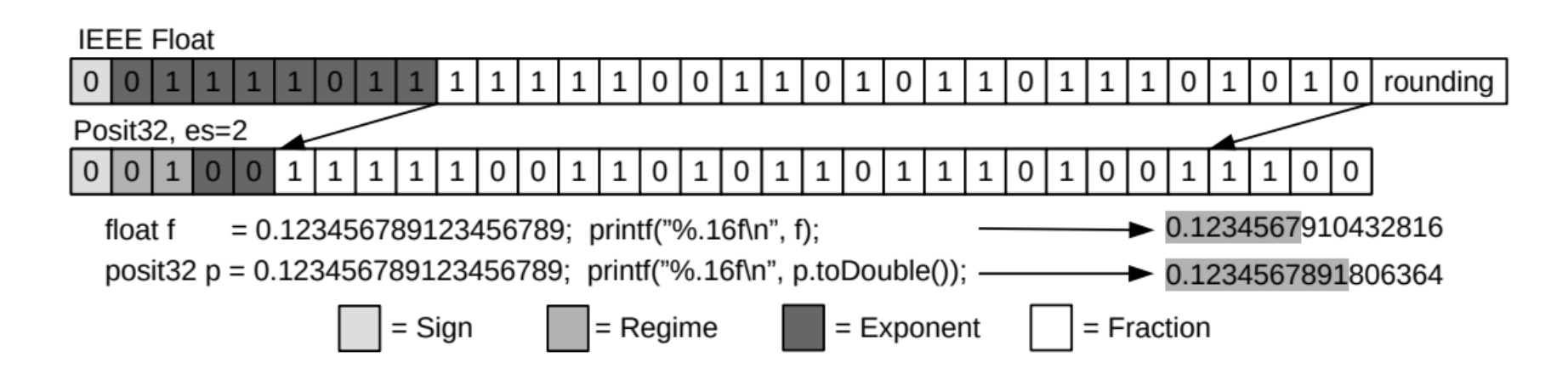
Emerging Floating-Point Formats for HPC
Floating-point operations are indispensable for many scientific applications. Their precision formats can significantly impact the power, energy consumption, memory footprint, performance, and accuracy
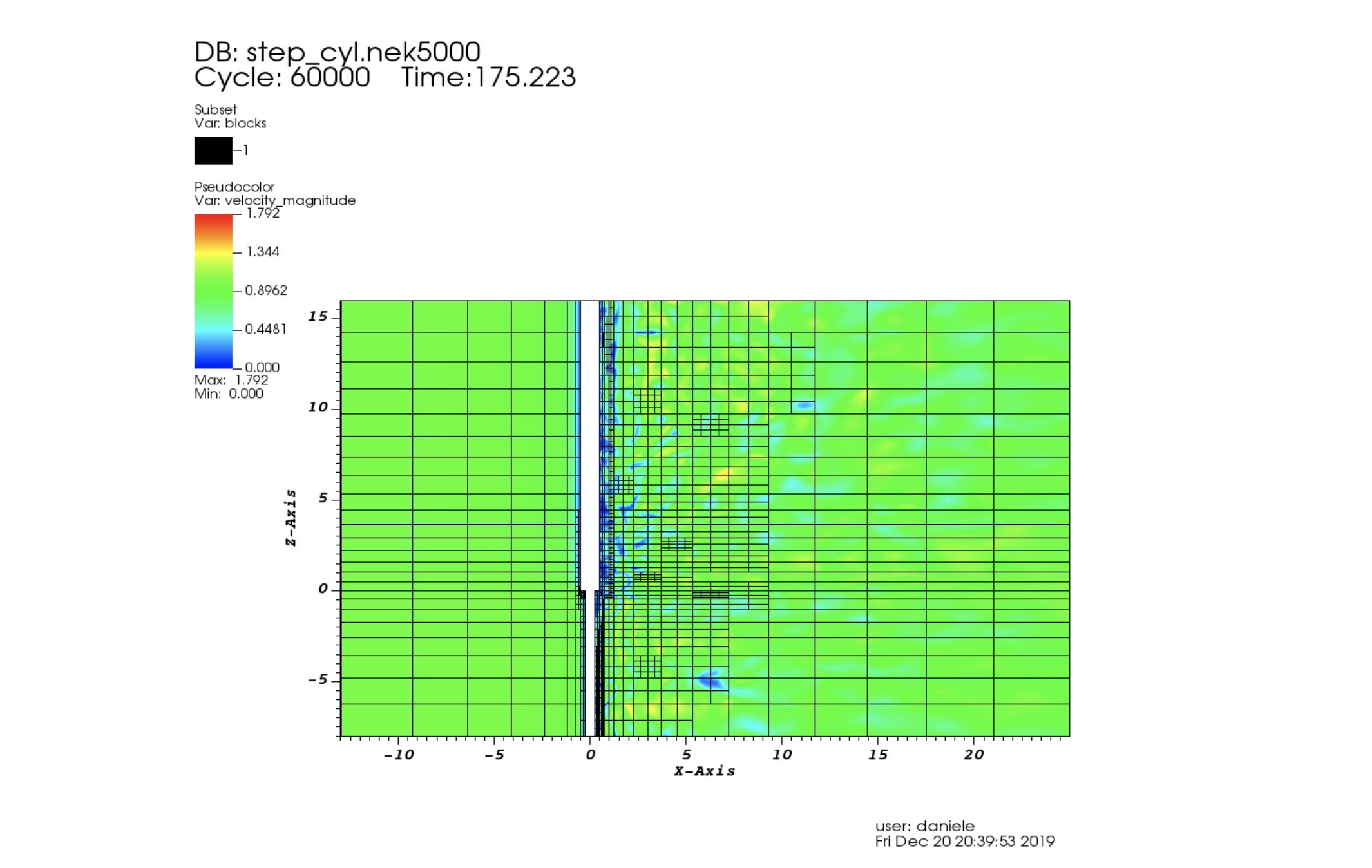
AMR for Nek5000
When we study turbulent chaotic flows in complicated geometries our experience could not be sufficient to suggest where a more refined mesh is required.

ABL: LES Workshop – May 2019
A series of presentations were given over a span of two days to identify the state-of-the-art of large- eddy simulations (LES)
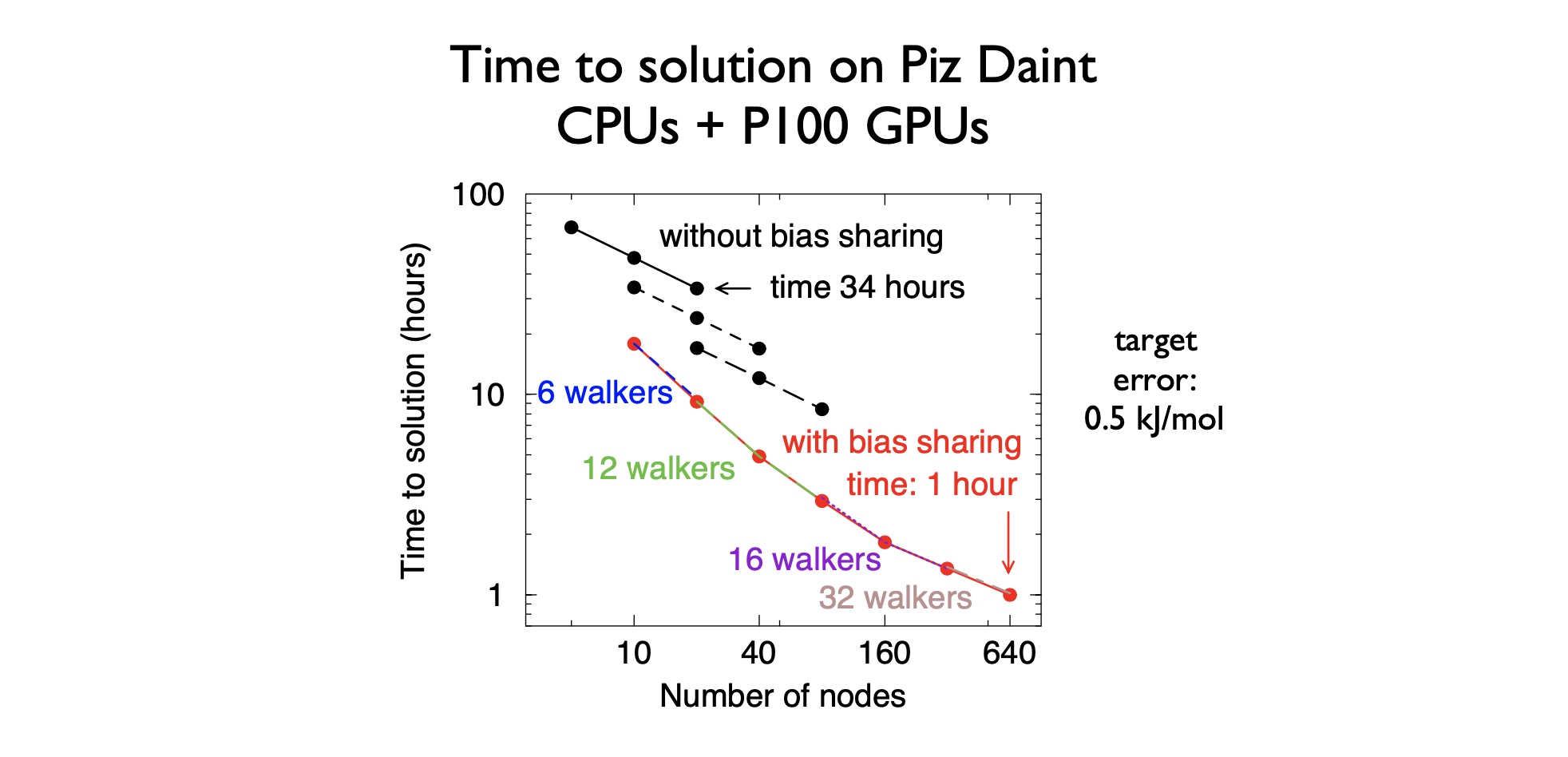
Ensemble parallelism in GROMACS
Scaling individual atomistic simulations of bio-molecules is strong scaling problem, as the molecules have fixed size.
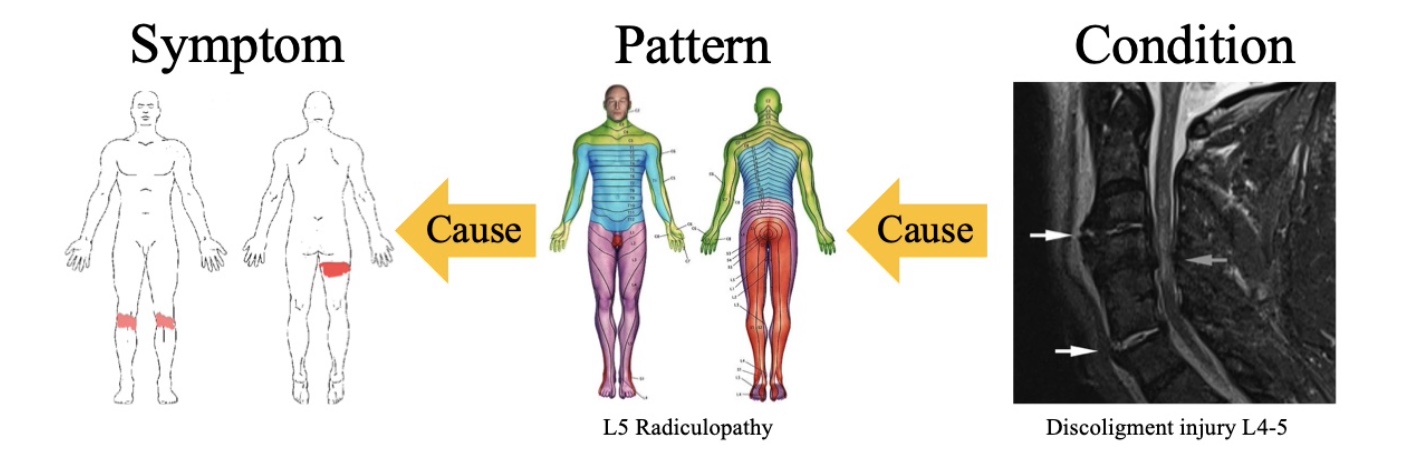
Developed methods for discovering cause and effect from medical data
Reasoning about cause and effect is an important aspect of human intelligence, and would thus constitute a valuable part of a medical diagnostics system.
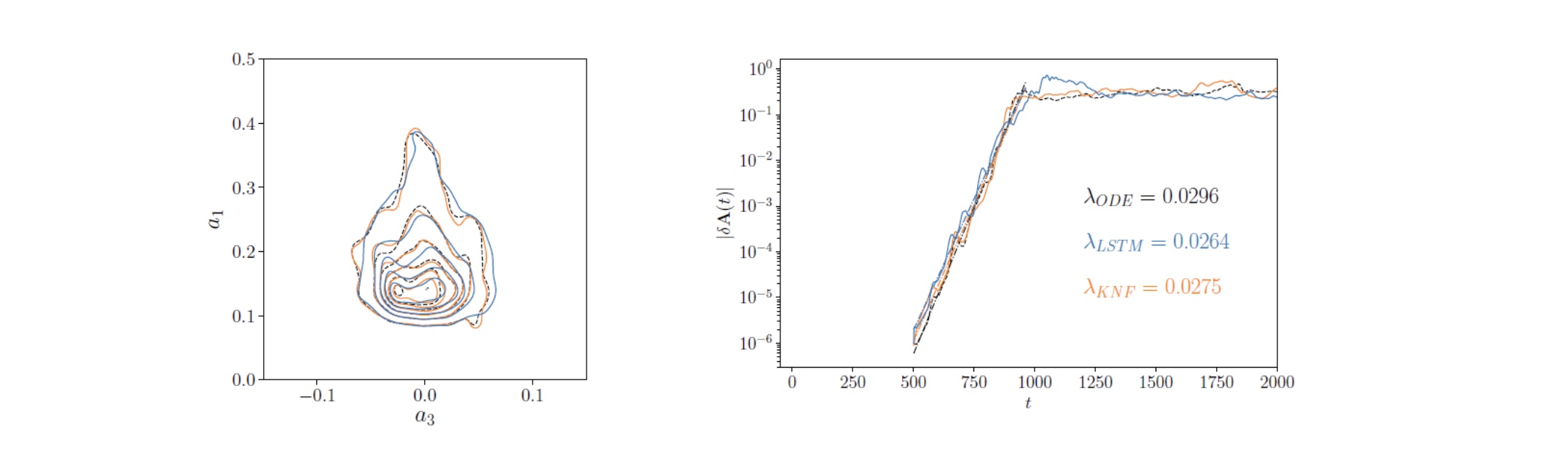
Pioneered the use of recurrent neural networks for temporal predictions in turbulent flows
SeRC researchers have assessed the prediction capabilities of long-short-term memory (LSTM) neural networks

Artificial intelligence for diagnosis and grading of prostate cancer in biopsies
We published an article entitled “Artificial intelligence for diagnosis and grading of prostate cancer in biopsies: a population-based, diagnostic study” in Lancet Oncology (https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(19)30738-7; impact factor=35).

Ontologies for the materials science domain
Ontologies standardize terminology in a domain and are a basis for semantically enriching data, integration of data from different databases, and reasoning over the data. They deal with the big data issues of Variety, Variability, and Veracity.
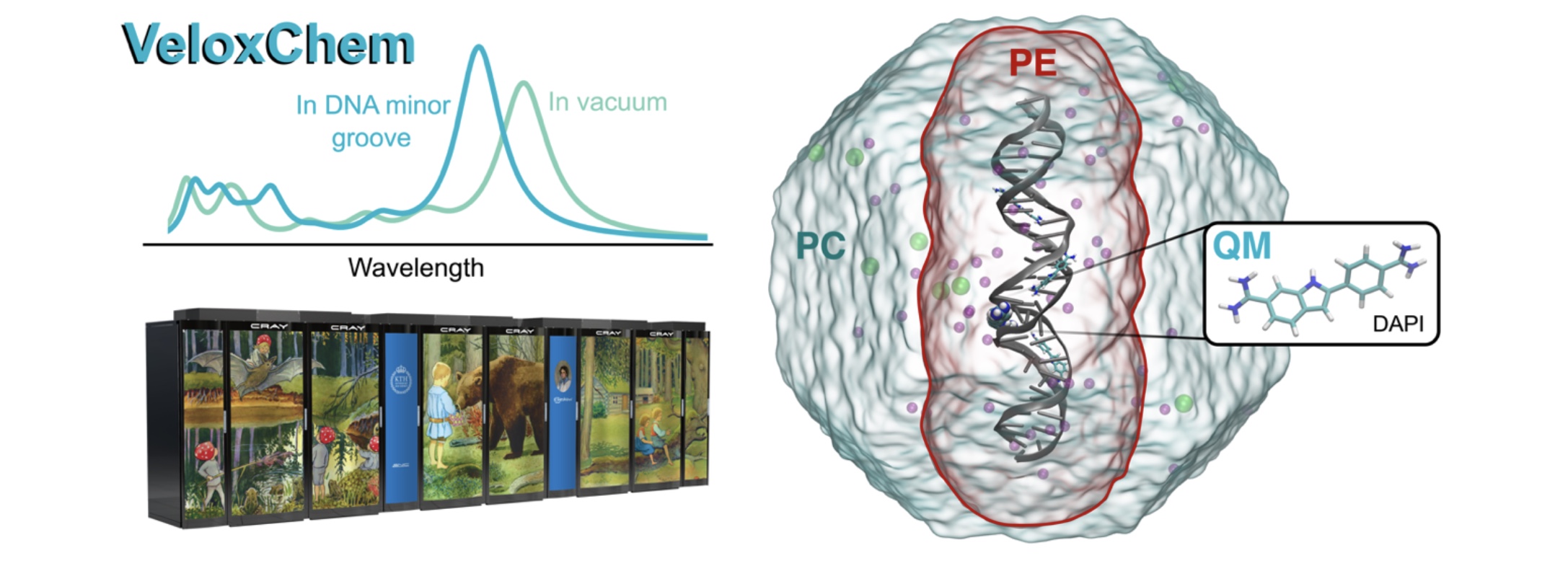
VeloxChem: Enabling Quantum Molecular Modeling in High-Performance Computing Environments
An open-source program named VeloxChem has been developed for the calculation of electronic real and complex linear response functions at the levels of Hartree–Fock and Kohn– Sham density functional theories.
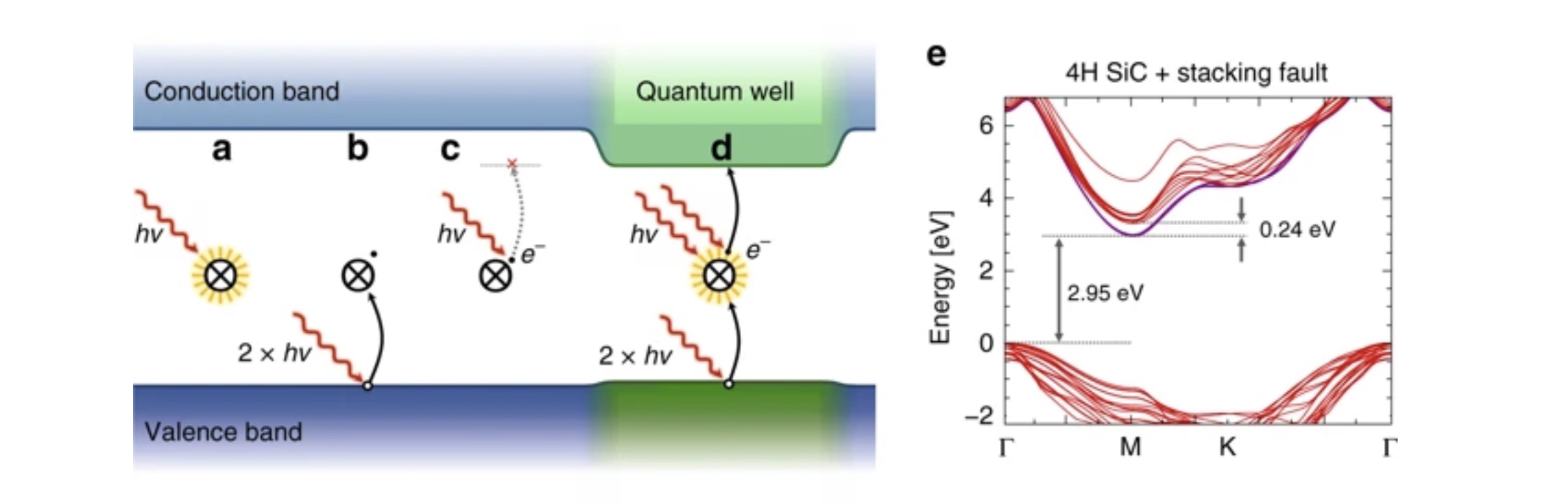
Stabilization of point-defect spin qubits by quantum wells
Defect-based quantum systems in wide bandgap semiconductors are strong candidates for scalable quantum-information technologies.
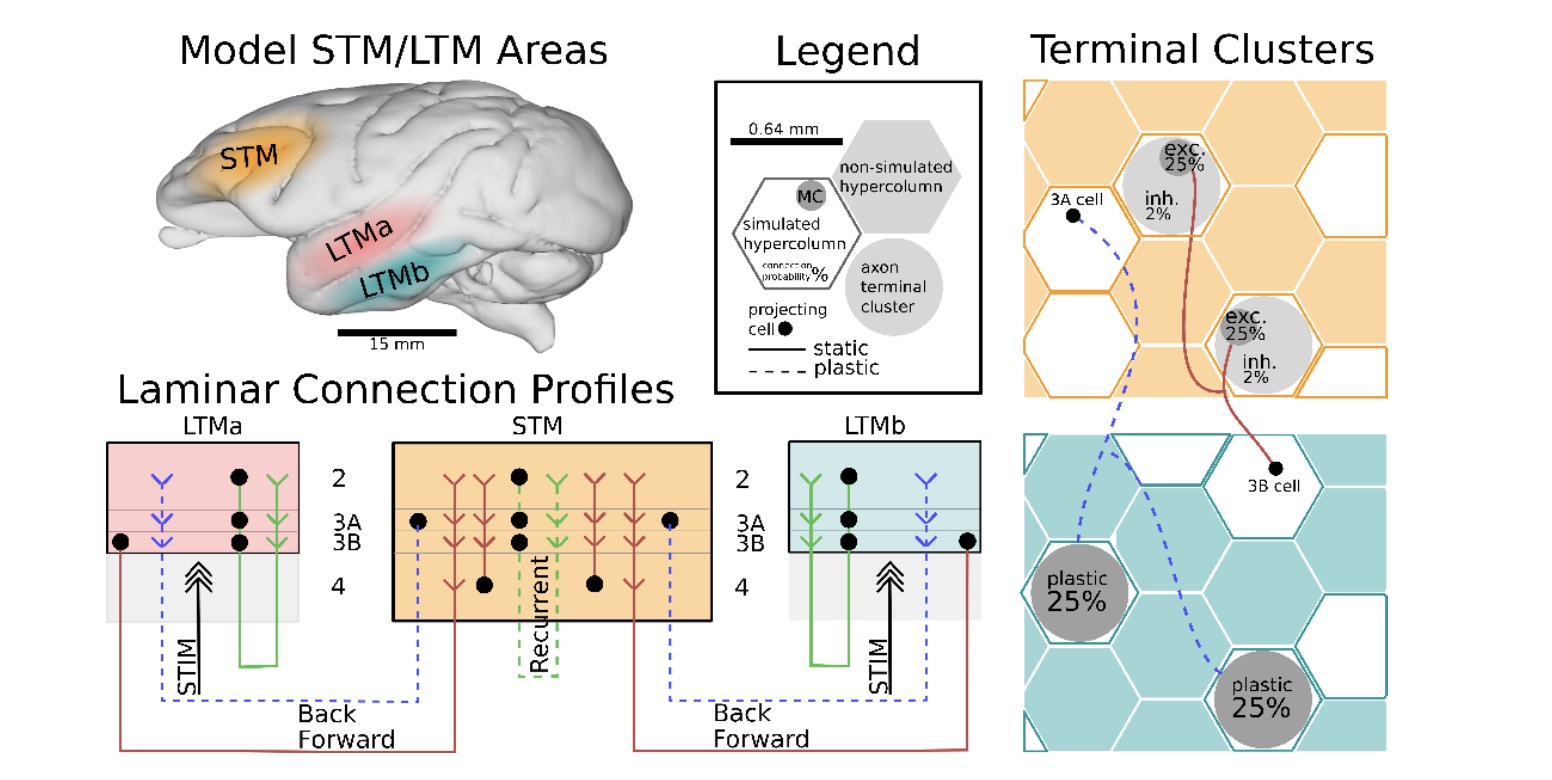
Synaptic theory of working memory explains most recent experimental findings about neural correlates of working memory
Our spiking neural network attractor memory model accounting for a synaptic theory of working memory has been validated using experimental data to explain the most recent observations about bursty nature of neuronal spiking as well as gamma- and beta-band oscillations of field potentials.
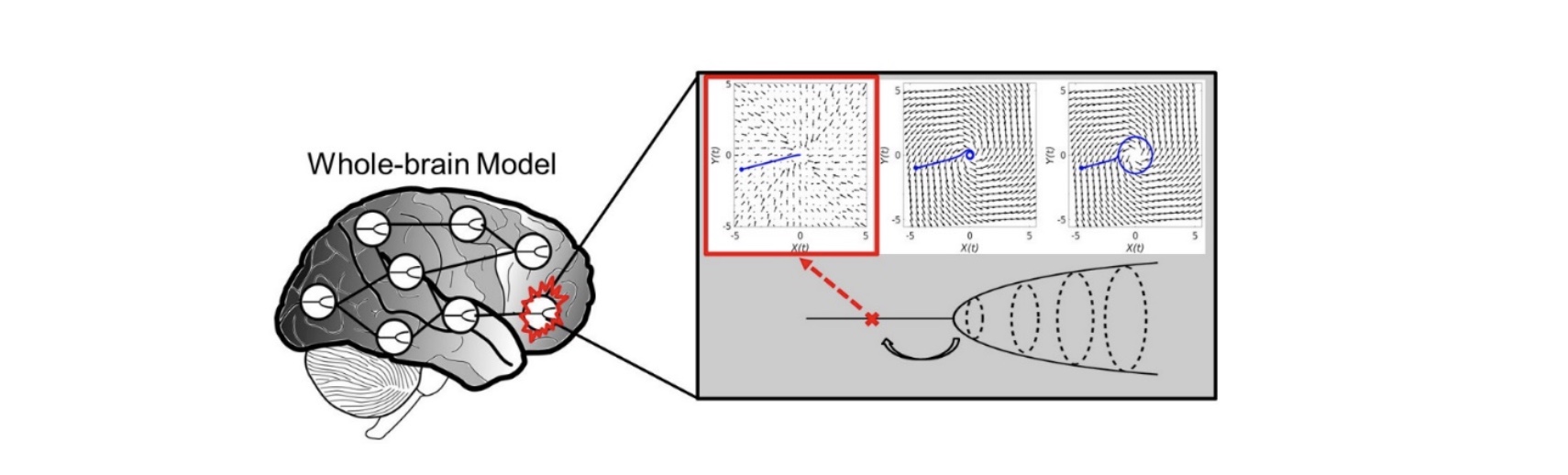
Predicting regional vulnerability in the brain using dynamic modeling of resting-state fMRI data
A new macroscopic computational model of brain oscillations in resting-state fMRI data was developed and evaluated. Results show that the effect of local lesions can be captured and studied by making regional changes in oscillation dynamics.
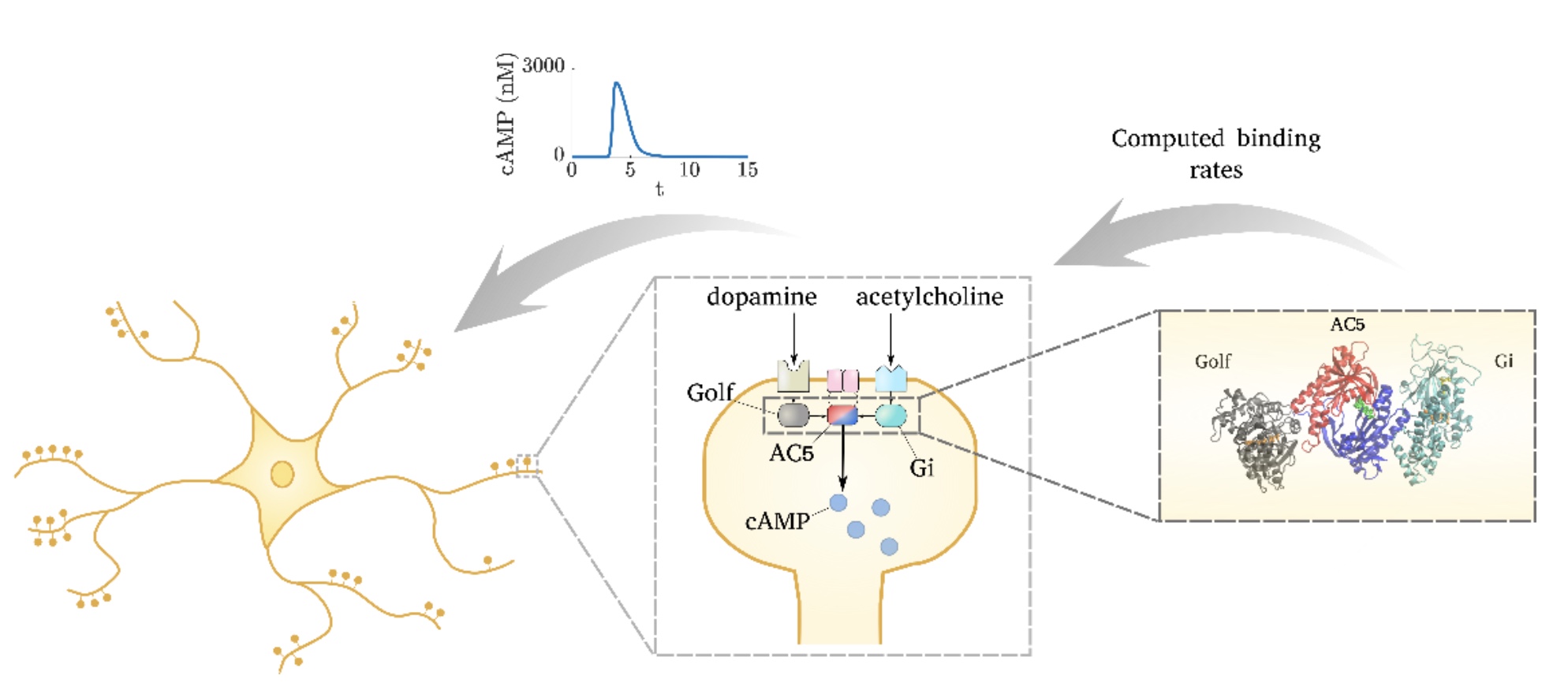
Adenylyl cyclase 5 in striatal neurons confers the ability to detect coincident neuromodulatory signals
We have demonstrated that molecular-level simulations can inform subcellular models of synaptic plasticity. Several computational tools, from molecular dynamics and Brownian dynamics simulations to bioinformatics approaches, were combined to constrain a kinetic model of the adenylyl cyclase type 5 (AC5)-dependent signaling system in the striatum.




