PSDE Highlight: An atlas of combinatorial transcriptional regulation in mice and man
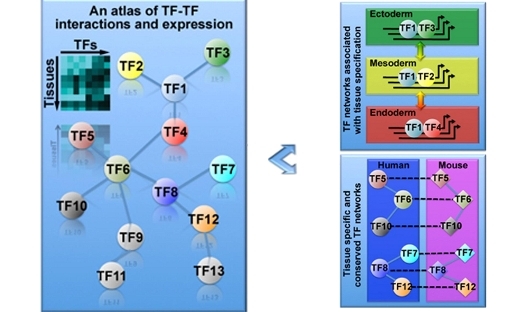
Availability of large TF combinatorial networks in both humans and mice will provide many opportunities to study gene regulation, tissue differentiation, and mammalian evolution.
Combinatorial interactions among transcription factors are critical for directing tissue-specific gene expression. To build a global atlas of these combinations, we have screened for physical interactions among the majority of human and mouse DNA-binding transcription factors (TFs). The complete networks contain 762 human and 877 mouse interactions. Analysis of the networks reveals that highly connected TFs are broadly expressed across tissues, and that roughly half of the measured interactions are conserved between mouse and human. The data highlight the importance of TF combinations for determining cell fate, and they lead to the identification of a SMAD3/FLI1 complex expressed during development of immunity. The availability of large TF combinatorial networks in both human and mouse will provide many opportunities to study gene regulation, tissue differentiation, and mammalian evolution.
References
Timothy Ravasi ,*1,2, Shintaro Katayama*3, Vladimir B. Bajic*4, Kai Tan*1#, Sebastian Schmeier4, Mutsumi Kanamori-Katayama3, Nicolas Bertin3, Piero Carninci3, Carsten O. Daub3, Alistair R. R. Forrest3,5, Julian Gough6, Sean Grimmond7, Jung-Hoon Han8, Takehiro Hashimoto3, Winston Hide4,9, Oliver Hofmann4, Mandeep Kaur4, Hideya Kawaji3, Timo Lassmann3, Erik van Nimwegen10, Cameron Ross MacPherson4, Chihiro Ogawa3, Aleksandar Radovanovic4, Ariel Schwartz1, Rohan D. Teasdale11, Jesper Tegnér12, 13, Sarah A. Teichmann8, David A. Hume7, 14, Trey Ideker†1 Riken Omics Science Center: Takahiro Arakawa3, Noriko Ninomiya3, Kayoko Murakami3, Michihira Tagami3, Shiro Fukuda3, Kengo Imamura3, Chikatoshi Kai3, Ryoko Ishihara3, Yayoi Kitazume3, Jun Kawai3 General Organizers: Harukazu Suzuki†3, Yoshihide Hayashizaki†3 (2010) “An atlas of combinatorial transcriptional regulation in mouse and man.”, The FANTOM consortium and RIKEN Omics Science Center (Genome Network Project, Expression Cluster Workshop): , Cell. 5;140(5):744-52.




